Boiling of water is a physical change rather than a chemical change as the water vapors retain the same molecular structure as liquid water after boiling. Boiling is a physical change in which molecules are not chemically altered.
Boiling of water is an important phenomenon to understand the properties of water.
This article answers the question ” Is boiling of water a chemical change?”.

Table of Contents
What Is the Boiling Point of Water?
At one atmosphere of pressure, the boiling point of water is 100 °C or 212 °F (sea level). The value, however, is not constant. The boiling point of water is affected by atmospheric pressure, which varies with elevation. Water boils at a lower temperature as you gain altitude (e.g., ascending a mountain), and it boils at a higher temperature as atmospheric pressure rises (coming back down to sea level or going below it).
The boiling point of water is also influenced by its purity. Impurities in water (such as salted water) cause it to boil at a higher temperature than pure water. This phenomenon is known as “boiling point elevation,” and it is one of the water’s colligative properties.
Is the boiling of water a chemical change?
The boiling of water is not a chemical change.
Boiling is a physical change. A physical change occurs when a substance undergoes a change in its physical properties. In most cases, a physical change can be reversed. There is no new substance formed as a result of such a change.
Examples of physical changes are boiling water, melting of ice, freezing of water, dissolving sugar and water, and shredding of paper.
When a liquid is heated to its boiling point, it turns into a vapor. The transition from liquid to gaseous occurs when the liquid’s vapor pressure equals the atmospheric pressure. Boiling is a physical change that does not affect molecules.
During boiling, bubbles and steam are formed when atoms or molecules spread out enough to change the state of a liquid from a liquid to a gaseous state.
The boiling point is the temperature at which a certain liquid starts to boil. At a pressure of 1 atm, water boils at 100oC. The temperature, the pressure of the air, and the vapor pressure of a liquid all affect how quickly a liquid will boil. When the pressure of the air meets the vapor pressure of the liquid, the liquid starts to boil.
Key Points
| The boiling point of water | 100 °C or 212 °F (sea level) |
| Formula of water | H2O |
| The melting point of water (ice) | 0 degrees Celsius (32 degrees F) |
| The specific gravity of water | 1 at 4 degrees Celsius (no units) |
| Viscosity of water | 0.01 poise or 0.001 Pa.s (Pascal seconds) at 0 degrees Celsius |
Temperature and Boiling
When boiling occurs, the more energetic molecules become gases, spread out, and form bubbles.
These bubbles rise to the surface and are carried into the atmosphere.
The energy required to convert a liquid to a gas is called the enthalpy of vaporization.
Furthermore, the thermal energy in the liquid is removed by gas molecules leaving the liquid.
As a result, the temperature of the liquid remains constant during the boiling process.
For example, while boiling, water will remain at 100oC (at a pressure of 1 atm or 101.3 kPa).
A heating curve is a graph of temperature vs. time for water changing from a liquid to a gas that shows a constant temperature as long as the water is boiling.
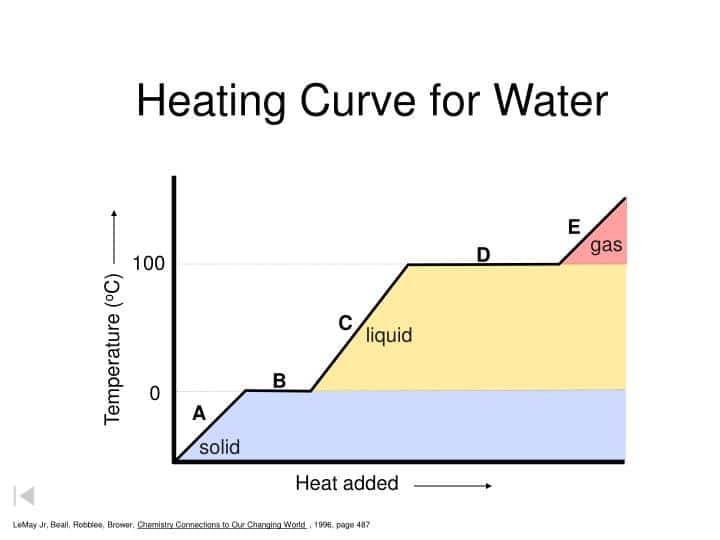
The heating curve of water shows that the temperature of H2O will exceed 100 oC only after it has completely changed to the gaseous phase. The temperature will remain constant as long as there is liquid.
The boiling point of a liquid is affected by the pressure of a gas above it. In an open system, this is referred to as atmospheric pressure. The higher the pressure, the more energy is required to boil liquids and the higher the boiling point.
Higher Atmospheric Pressure = More Energy Needed to Boil = Higher Boiling Point
In an open system, this is represented by air molecules colliding with the liquid’s surface and creating pressure. This pressure spreads throughout the liquid, making it more difficult for bubbles to form and boiling to occur. Reduced pressure requires less energy to convert a liquid to a gaseous phase, and boiling occurs at a lower temperature.
When molecules evaporating from a liquid collide with air molecules, they create upward pressure. “The vapor pressure” is the term given to this upward push. Different substances have varying vapor pressures and, as a result, varying boiling points. This is due to the fact that molecules have different intermolecular forces.
A liquid’s vapor pressure reduces the amount of pressure exerted on it by the atmosphere. As a result, high vapor pressure liquids have lower boiling points. By heating a liquid and causing more molecules to enter the atmosphere, vapor pressure can be increased. When the vapor pressure equals the atmospheric pressure, boiling will begin. Without any external pressure, the liquid molecules will be able to spread out and transition from a liquid to a gaseous state. The gas will rise to the surface like bubbles in the liquid and be released into the atmosphere.
What is a chemical change?
When one or more compounds, known as reactants, are converted into one or more distinct substances, known as products, a chemical reaction occurs. Substances include chemical elements and compounds. In a chemical reaction, the constituent atoms of the reactants are rearranged, resulting in the formation of various substances as products. The number of atoms before and after the chemical transformation is the same, but the number of molecules is different.
Examples of Chemical Reactions in Everyday Life
- Cooking
- Photosynthesis
- Cellular respiration
- Corrosion
- Digestion
- Fireworks
- Bleaching
Summary
- The answer to the question ” is boiling water a chemical change“? is No.
- Water boiling is a physical change as boiling water vapors retain the same molecular structure as liquid water.
- When water boils, the more energetic molecules turn into gases, spread out, and form bubbles.
- During the boiling process, the liquid’s temperature remains constant.
Related Links
Thermal Conductivity of Water
The Specific Gravity of Water
The Density of Water lbs/U.S gal
Specific Heat of Water
Physical and Chemical Properties of Water
Exam Related Questions
| # | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Is boiling of water a chemical change? | No, boiling of water is a physical change. |
| 2. | What happens to the chemical composition of water when it boils? | There is no change in the chemical composition. |
| 3. | Which physical state of water has the highest energy level of molecules? | Water in the gas state (steam) has the highest energy level of molecules. |
| 4. | What is the boiling point of water at standard atmospheric pressure? | The boiling point of water at standard atmospheric pressure is 100°C or 212°F. |
| 5. | Is the boiling point of water affected by altitude? | Yes, the boiling point of water decreases as altitude increases. |
| 6. | Is boiling of water a reversible process? | Yes, boiling of water is a reversible process. |
| 7. | Can boiling water cause a chemical reaction? | Boiling water itself does not cause a chemical reaction. |
| 8. | Does boiling water remove impurities or contaminants? | Boiling water can remove some impurities or contaminants, but not all. |
| 9. | Can boiling water change the taste of the water? | Boiling water can sometimes change the taste of the water. |
| 10. | How does the boiling of water relate to the water cycle? | Boiling of water is one step in the water cycle, where water evaporates from bodies of water and forms clouds in the atmosphere. |
| 11. | Which type of energy is involved in the boiling of water? | The energy involved in the boiling of water is thermal energy. |
| 12. | Is the boiling of water an exothermic or endothermic process? | The boiling of water is an endothermic process. |
| 13. | What is the process called when water vapor turns directly into ice without passing through the liquid phase? | The process is called sublimation. |
| 14. | Can boiling water be used to sterilize equipment or surfaces? | Yes, boiling water can be used to sterilize equipment or surfaces. |
| 15. | Can boiling water cause burns or scalds? | Yes, boiling water can cause burns or scalds. |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the specific heat of water?
Specific heat refers to the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one Celsius degree. Specific heat is usually measured in calories or joules per gram per Celsius degree. For instance, water has a specific heat of 1 calorie (or 4.186 joules) per gram per Celsius degree.
2. Is water vapor a greenhouse gas?
Yes, water vapors are greenhouse gases. Other examples are listed below:
- Carbon dioxide
- Methane
- Ozone
- Nitrous oxide
- Chlorofluorocarbons
3. What is the density of water?
At 4.0°C (39.2°F), the density of water in g/ml is 0.9998395. This is equivalent to one gram per milliliter (g/ml) or one gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm3). Check full article density of water g/ml.
4. How many cups are in a gallon?
A US liquid gallon is equal to 16 cups, while a US dry gallon is equal to 18.61 cups. In the United States, one cup equals half a pint (236.6 ml). Check out the full article, “How many cups are in a gallon”.
5. How many water bottles is a gallon?
7.58 bottles of water equal one gallon in the United States, and 9.10 bottles of water equal one gallon in the United Kingdom. Check the full article here“how many water bottles is a gallon”.
6. How can water be boiled without heating?
Water can be boiled without being heated. Since the boiling point of a liquid is affected by temperature, ambient pressure, and the liquid’s vapor pressure.
By raising the pressure on the surface of the water inside a closed, insulated vessel, the boiling point of water may be reduced to room temperature.
7. Why does the temperature of boiling water not change?
The temperature of the water does not vary during boiling because all of the heat energy supplied is used up in changing the state of water from liquid to gaseous water vapor.
More Interesting Topics
Sulfur Electron Configuration
How many valence electrons does iron have?
Diffusion Coefficient| Mass Diffusivity
Dynamic Viscosity-An Overview
Hydrogen Bond| Definition & Easy Explanation
How Much Does a Gallon of Water Weigh?
Sublimation Examples| Process & Case Study
- BCl3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - November 1, 2023
- PH3 Lewis Structure in four simple steps - October 8, 2023
- PF3 Lewis structure in four simple steps - September 24, 2023



